Abstract: re evaluation of policies and practices to ensure their effectiveness in a virtual environment, encompassing recruitment, performance management, and employee engagement strategies. The rise of e-commerce and the integration of digital technologies have also shifted workforce demands, emphasizing the need for digital literacy and competencies in virtual customer interactions.
These evolving dynamics underscore the need for HR professionals to not only adapt to the changing digital landscape but also emerge as strategic partners in guiding their organizations through this period of digital transition. As Accenture Research notes, the integration of generative AI in HR functions exemplifies this shift, offering new avenues for efficiency and strategic insights. The expanded role of HR in the digital era includes managing digital transformation, fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptability, and prioritizing employee well-being in a predominantly virtual work environment.
The digital revolution, accelerated by the global health crisis, has compelled organizations to redefine the workplace, prioritizing agility and adaptability.
As the McKinsey Global Institute highlights, this rapid change has blurred the boundaries in business practices – geographically, operationally, and culturally, demanding a more agile approach to work. The pre-pandemic rise of digital transformation was significantly expedited by COVID-19, propelling organizations worldwide to a critical juncture: swiftly adapt to remote work, leverage e-commerce platforms, and embrace digital communication tools, or risk falling behind.
The role of Human Resources (HR) has been pivotal in navigating and managing these changes. Traditional HR practices, once grounded in face-to-face interactions, have undergone substantial modifications. The transition to remote work has necessitated a comprehensive reevaluation of policies and practices to ensure their effectiveness in a virtual environment, encompassing recruitment, performance management, and employee engagement strategies. The rise of e-commerce and the integration of digital technologies have also shifted workforce demands, emphasizing the need for digital literacy and competencies in virtual customer interactions.
These evolving dynamics underscore the need for HR professionals to not only adapt to the changing digital landscape but also emerge as strategic partners in guiding their organizations through this period of digital transition. As Accenture Research notes, the integration of generative AI in HR functions exemplifies this shift, offering new avenues for efficiency and strategic insights. The expanded role of HR in the digital era includes managing digital transformation, fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptability, and prioritizing employee well-being in a predominantly virtual work environment.
As we navigate the complexities of this digital era, the evolving role of HR becomes increasingly critical. The pandemic has not only hastened the digital transformation of the workplace but also redefined the expectations and responsibilities of HR professionals, marking a new chapter in the field of human resources management.
Digitalization and Human Resources
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI), particularly generative AI models like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, into Human Resources (HR) represents a significant paradigm shift in workforce management and employee relations. Far from being a mere trend, AI has become integral to enhancing efficiency, strategic insights, and employee experiences in HR practices. This transformation covers a wide range of HR functions, including recruitment, employee engagement, and performance management, aligning with the digital and AI-driven transformation of the workplace.
AI in HR Functions
In recruitment, AI’s impact is evident. Generative AI tools have transformed traditional recruitment processes, enabling HR professionals to efficiently analyze a wide array of applicant data, including resumes and social media profiles. This technology significantly streamlines the candidate screening process, allowing for more strategic talent acquisition approaches.

Employee engagement has also evolved due to AI applications. AI-driven chatbots and platforms offer immediate, tailored responses to employee inquiries, facilitating real-time feedback and insights into workforce morale. Furthermore, AI enables personalized employee development, suggesting training opportunities based on individual performance metrics and career aspirations.
In performance management, AI contributes to more objective and data-driven approaches. Advanced analytics help track and evaluate employee performance, providing fair and unbiased evaluations and predicting future performance trends, crucial for succession planning and identifying potential leaders.
Practical Examples and Challenges
A prime example of AI’s application in HR is the use of generative AI technologies like ChatGPT. This advanced AI model revolutionizes various HR functions, particularly in talent acquisition, by efficiently matching candidates to job roles and enhancing recruitment processes. ChatGPT’s capabilities extend to engaging with candidates and generating personalized communications, thus maintaining a positive candidate experience throughout the recruitment process.
The use of generative AI in HR also extends to employee training and development, where ChatGPT can develop customized training content tailored to specific job roles and individual learning needs.
However, the integration of AI into HR is not without challenges. Addressing potential biases in AI algorithms is crucial, necessitating the use of diverse training datasets and regular audits. Additionally, it’s important to mitigate concerns about AI replacing human jobs by emphasizing AI’s role in augmenting human capabilities.
In conclusion, the integration of generative AI, particularly models like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, marks a significant advancement in HR, offering more efficient, personalized, and unbiased processes. This evolution is vital in optimizing talent acquisition and enhancing the overall employee experience, from recruitment to development, aligning with the transformative digital era in the workplace.
Innovation Cycles and HR Dynamics
Schumpeter’s concept of Creative Destruction depicts capitalism as a dynamic force, continuously revolutionizing the economic structure from within, where innovative business models consistently render established ones obsolete. This framework is highly relevant to today’s rapidly evolving job market, signifying that each advancement in technology fundamentally reshapes the professional landscape, phasing out legacy roles and catalyzing the creation of new positions in emergent fields.
Navigating Through Innovation Cycles

The evolution of innovation cycles, especially the rapid progression into the Sixth Wave characterized by AI, IoT, robotics, and clean tech, denotes a significant shift in occupational roles. Emerging technologies have given rise to a demand for expertise in AI, data analytics, and digital marketing, gradually eclipsing roles that were once fundamental to the economic structure. It is imperative for HR professionals to strategically anticipate these shifts. Staying current with industry trends and technological advancements becomes crucial for HR to prepare the workforce for the in-demand skills of the future and to ensure the organization’s resilience in the face of constant change.
HR’s Strategy for Continuous Evolution
In response to the relentless waves of innovation depicted in the timeline, HR must champion a culture of adaptability and resilience. By cultivating an environment that not only anticipates but also embraces change, HR can facilitate the workforce’s transition to new roles and technologies. This era of innovation necessitates a philosophy of continuous learning and development, laying the groundwork for reskilling and upskilling initiatives.
HR is tasked with forging partnerships with educational entities and pinpointing internal opportunities for skill development, such as cross-functional projects or mentorship arrangements. Moreover, performance management systems must evolve to support these developmental goals, creating incentives for acquiring new skills and knowledge.
In summary, Schumpeter’s Theory of Creative Destruction urges HR to take a visionary stance, strategically steering workforce capabilities to adeptly navigate the currents of innovation. By advocating for adaptability, endorsing ongoing education, and emphasizing skill enhancement, HR can adeptly guide organizations through the ever-shifting terrain of the job market, preparing both employees and businesses to confidently face the future.
The Componential Theory and Its Impact on HR Innovation
Teresa Amabile’s Componential Theory of Organizational Creativity and Innovation articulates that creativity in organizations emerges from the synergy of expertise, innovative thinking capabilities, and intrinsic motivation, all amplified or inhibited by the supporting work environment. This paradigm highlights the pivotal role of a conducive corporate atmosphere in transforming individual creativity into organizational innovation.
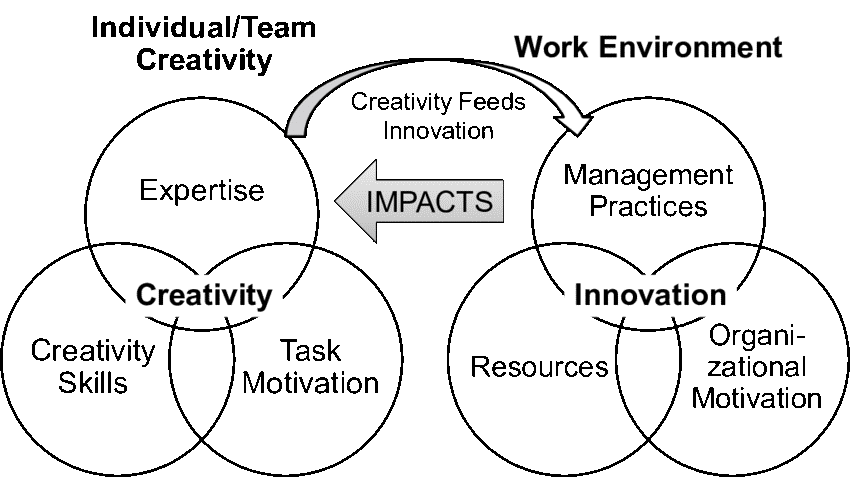
Synergy of Creativity and Environment in HR
Expertise refers to the knowledge, technical skills, and talents that individuals contribute to their work. Creative thinking skills represent the capacity for flexibility and ingenuity in problem-solving. However, it is intrinsic motivation—employees’ deep personal interest and engagement in their tasks—that is the lifeblood of creativity. The theory further explains that the work environment dramatically influences these components, suggesting that workplaces that provide autonomy, endorse risk-taking, and value each individual’s input are likely to see a greater conversion of creativity into innovation.
HR’s Role in Cultivating a Creative Ecosystem
In shaping a work environment conducive to creativity and innovation, HR strategies must concentrate on:
- Developing Expertise: Through comprehensive learning and development initiatives, employees are encouraged to refine and expand their skill sets.
- Promoting Creative Thinking: HR can cultivate a culture that celebrates creativity, facilitated by brainstorming sessions and encouraging diverse thinking.
- Boosting Intrinsic Motivation: HR can foster an intrinsically motivated workforce by providing meaningful work, autonomy, and due recognition.
- Supporting Work Environment: By creating a space that allows for experimentation and the sharing of ideas, organizations enable employees to innovate without the fear of failure.
Real-World Applications
In the modern context, companies such as Tesla have become a paragon of Amabile’s theory in action, particularly in the way they champion innovation. Tesla’s culture of encouraging its engineers and designers to push boundaries in electric vehicles and sustainable energy solutions exemplifies a commitment to creativity and innovation. Similarly, tech giant Adobe has implemented programs like the Adobe Kickbox, which provides employees with resources to develop their creative ideas into prototypes, demonstrating HR’s role in fostering an innovative work culture.
These contemporary instances illustrate the power of HR in shaping environments that not only encourage the development of expertise and creative thinking but also deeply embed intrinsic motivation in the workplace culture. By doing so, HR leaders are pivotal in steering their organizations towards a future where creativity and innovation are not just encouraged but embedded in the very fabric of the organizational structure.
The T-Shaped Professional Approach in Talent Management
The evolving dynamics of talent management emphasize the cultivation of T-shaped professionals—individuals with deep expertise in a specific discipline, bolstered by a breadth of skills enabling them to interface across various fields effectively. Skills such as teamwork, communication, and critical thinking are increasingly vital in today’s fast-paced, technology-driven workplace. This T-shaped model is particularly resonant in an era marked by the rapid digitalization of industries and the continuous innovation described by Schumpeter’s Theory of Creative Destruction.
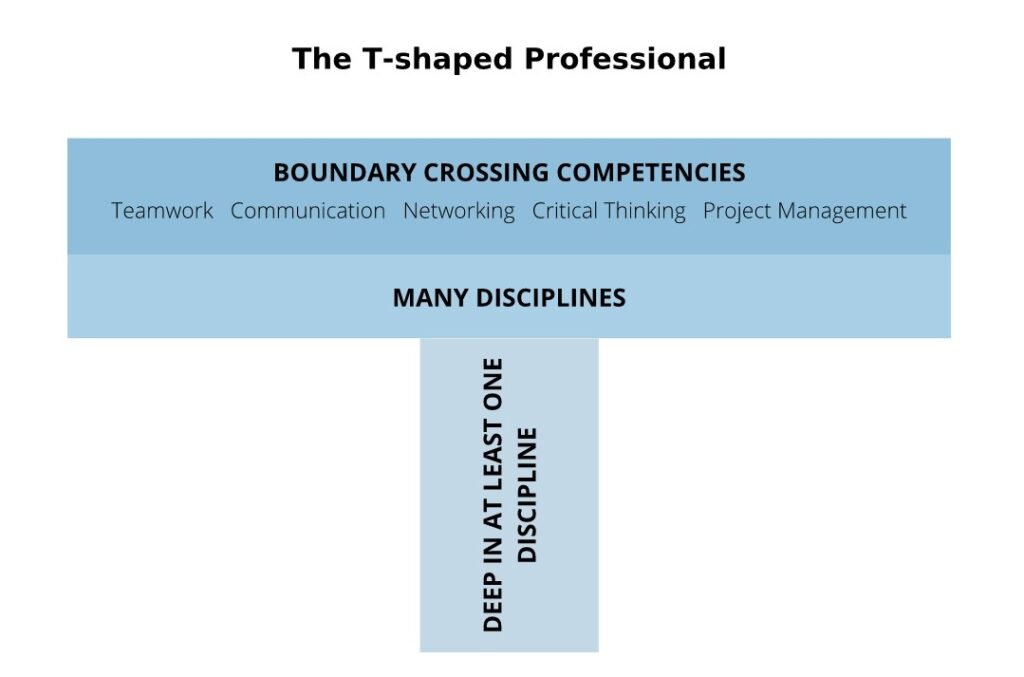
Multidisciplinary Teams as Innovation Catalysts
HR’s strategic development of T-shaped professionals involves orchestrating multidisciplinary teams that meld specialized knowledge with versatile, cross-functional competencies. This is integral to nurturing a work culture that prizes innovation and collaborative problem-solving—a crucial edge in a market landscape perennially altered by new technological waves (Hammer et al., 2021).
In the landscape of modern business, HR’s strategies for fostering T-shaped talent are multifaceted and dynamic. These strategies begin with:
Multidisciplinary Teams as Innovation Catalysts
HR’s strategic development of T-shaped professionals involves orchestrating multidisciplinary teams that meld specialized knowledge with versatile, cross-functional competencies. This is integral to nurturing a work culture that prizes innovation and collaborative problem-solving—a crucial edge in a market landscape perennially altered by new technological waves.
In the landscape of modern business, HR’s strategies for fostering T-shaped talent are multifaceted and dynamic. These strategies begin with:
- Diverse Team Composition: Focus on creating teams with a diverse blend of expertise, cultural backgrounds, and perspectives. This diversity acts as a catalyst for innovative thinking and inventive problem-solving.
- Collaborative Culture: Foster an organizational culture where collaboration is the norm. Encourage the establishment of common objectives and open communication, supported by initiatives and tools designed to enhance team dynamics.
- Cross-disciplinary Interaction: Actively encourage and facilitate projects that necessitate teamwork across different functional areas, broadening employees’ understanding and exposing them to varied experiences and knowledge pools.
Transitioning to the realm of organizational learning, which is pivotal in today’s T-shaped professional model, the focus shifts to:
- Expansive Learning Ecosystem: Implement a comprehensive range of learning opportunities encompassing interactive workshops, digital e-learning platforms, and microlearning experiences. This approach ensures employees access diverse educational resources for skill acquisition and refinement.
- Mentorship and Coaching Programs: Develop structured mentorship and coaching initiatives that facilitate the transfer of expertise and provide tailored professional guidance, fostering a culture of knowledge-sharing and personal development.
- Constructive Feedback Culture: Create an organizational culture that prioritizes constructive feedback. Establish systems and processes that encourage open dialogue and recognition, supporting each employee’s developmental journey and reinforcing their value within the organization.
In the fast-evolving business environment, effective talent development strategies are imperative. These include:
- Personalized Development Roadmaps: Initiate meaningful career development conversations to align individual ambitions with the company’s strategic objectives. This approach involves crafting tailored development plans that pinpoint opportunities for professional growth and align with the individual’s career trajectory.
- Agile Performance Management: Adopt a proactive and dynamic approach to performance management. This involves transitioning from traditional evaluation methods to a model that emphasizes continuous feedback and recognition, fostering a culture of ongoing development and achievement.
- Enhanced Focus on Employee Well-being: Prioritize employee wellness by implementing flexible work policies and comprehensive wellness programs. This commitment to well-being supports a healthy work-life balance, contributing significantly to employee satisfaction, engagement, and overall productivity.
The commitment to developing T-shaped professionals is central to modern talent management. This strategy not only attracts exceptional talent but also nurtures and retains them, ensuring a robust, future-ready workforce that can thrive amidst the complexities and demands of the contemporary business landscape.
Conclusion
“Shaping the Future of Work: The Impact of Digital and AI on Human Resource Transformation” encapsulates the profound shift in the HR landscape, driven by digitalization and the adoption of generative AI technologies like ChatGPT. This article has navigated through the challenges and transformations in HR catalyzed by the global pandemic and the subsequent acceleration towards a digital-first approach in business practices. It highlights the essential role of HR in steering organizations through these paradigm shifts, ensuring the adaptation and implementation of policies that are attuned to a virtualized work environment.
The discussion extends to the significance of AI in redefining HR functions, from recruitment to employee engagement and performance management, by providing strategic insights, enhanced efficiency, and improved employee experiences. The introduction of generative AI models into HR practices offers a glimpse into a future where HR is not merely a support function but a strategic partner equipped with data-driven tools and insights.
The application of the Theory of Creative Destruction and the Componential Theory of Organizational Creativity and Innovation offers a theoretical framework to comprehend the evolving job market and highlights HR’s proactive role in nurturing an innovative and adaptable workforce. In the face of continual technological advancements, HR professionals are encouraged to foster a culture of continuous learning and adaptability, preparing employees to thrive amidst the demands of an ever-evolving business environment.
In essence, the article calls for HR leaders to embrace the transformative potential of digital and AI technologies, positioning themselves at the forefront of organizational change. By leveraging these tools, HR can guide their organizations towards sustained growth and resilience, ensuring a future-ready workforce capable of navigating the complexities of the digital era with confidence and creativity.
Reference
- Accenture Research. (2023). A new era of generative AI for everyone. https://www.accenture.com/content/dam/accenture/final/accenture-com/document/Accenture-A-New-Era-of-Generative-AI-for-Everyone.pdf.
- Amabile, T. M. (1983). The Social Psychology of Creativity: A Componential Conceptualization. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 45(2), 357-376.
- Amabile, T. M. (1996). Creativity in context: Update to the social psychology of creativity. Westview Press.
- Amabile, T. M., & Kramer, S. J. (2011). The Progress Principle: Using Small Wins to Ignite Joy, Engagement, and Creativity at Work. Harvard Business Review Press.
- Hammer, M., Harris, M., Ramnane, K., & Blackwell, E. (2021, July 19). Ops 4.0—The Human Factor: A class size of 1. McKinsey & Company. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/operations/our-insights/operations-blog/ops-40-the-human-factor-a-class-size-of-1
- McKinsey Global Institute. (2021, February 18). The future of work after COVID-19. https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/future-of-work/the-future-of-work-after-covid-19.
- Neufeld, D. (2021, June 30). Long Waves: The History of Innovation Cycles. Visual Capitalist. https://www.visualcapitalist.com/the-history-of-innovation-cycles/
- Nobel, C. (2015, May 26). Corporate Field Researchers Share Tricks of the Trade. Harvard Business School Working Knowledge. Retrieved from https://hbswk.hbs.edu/item/corporate-field-researchers-share-tricks-of-the-trade
- Nobel, C. (2017, September 27). What Happens When Ordinary People Get Creative? Harvard Business School Working Knowledge. Retrieved from https://hbswk.hbs.edu/item/what-happens-when-ordinary-people-get-creative
- Schaffer, C., & Lipton, A. (2021, March 16). “Both/And” Leadership: Combining the Benefits of I- and T-Shaped Leaders. Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning. https://www.harvardbusiness.org/both-and-leadership-combining-the-benefits-of-i-and-t-shaped-leaders/
- Schumpeter, J. A. (1942). Capitalism, Socialism, and Democracy. Harper & Brothers.
- Wale, H. (n.d.). T-Shaped Skills. Corporate Finance Institute. Retrieved from https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/management/t-shaped-skills/
- World Economic Forum. (2023). The future of jobs report 2023. https://www.weforum.org/publications/the-future-of-jobs-report-2023/.











Shaping the Future of Work:The Impact of Digital and AI on Human Resource Transformation – Global HR News & Updates
bvgxfmlnhd http://www.gm7121b761w3o7eu6uajy559n4n8nob3s.org/
[url=http://www.gm7121b761w3o7eu6uajy559n4n8nob3s.org/]ubvgxfmlnhd[/url]
abvgxfmlnhd